If you are in the manufacturing industry or involved in fluid control, you might have come across plug valves. They are commonly used to regulate flow in pipelines and are known for their tight sealing capabilities. But how do they work? In this article, we will take a deep dive into plug valves – starting from what they are, their components, and how they function. We will explore different types of plug valves and materials used to construct them. We will also discuss the advantages, disadvantages, and applications of plug valves so that you can decide if it’s the right valve type for your project. Join us as we demystify the working principle of plug valves!
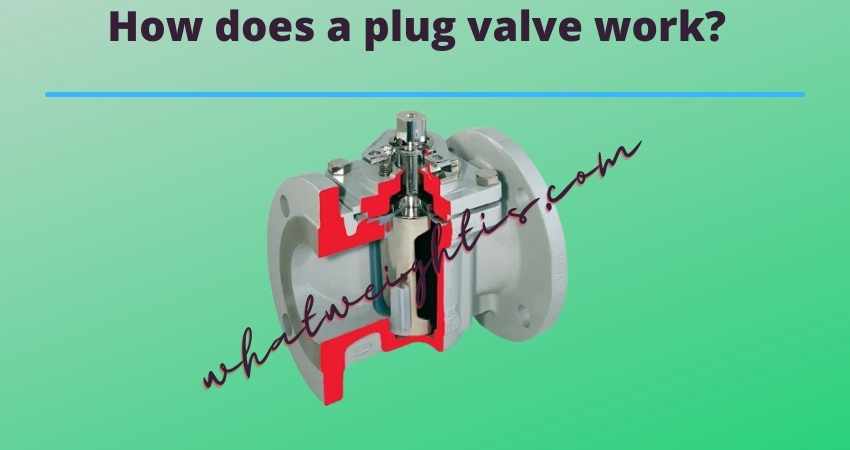
Overview of Plug Valves
Plug valves are a type of valve that uses a cylindrical or tapered plug to control the flow of fluid through the body. They are suitable for on-off, throttling, and diverting services. There are four major types of plug valves: lubricated and non-lubricated, eccentric, and expanding plug valves. Plug valves have a straight-through full port opening and can be used as replacements for gate valves in existing process services.
ANSI Standard B16.10 is the face-to-face standard for plug valves, but some manufacturers use face-to-face dimensions provided for gate valves. To get an in-depth understanding of how plug valves work, you can take Introduction to Valves Online Video Course. Overall, plug valves are versatile and reliable devices that play a crucial role in controlling fluid flow in industrial applications.
Components of a Plug Valve
Plug valves control fluid flow by rotating a cylinder or cone-shaped valve. The valve body contains one or more ports that allow fluid to pass through when the valve is open. Plug valves can be cylindrical or conically tapered with different sealing mechanisms. The earliest versions used direct contact which resulted in poor sealing and high opening/closing force. The design of plug valves has evolved to include lubricated, non-lubricated, multi-port, eccentric, and expanding types. Compared to other types of valves, plug valves are relatively cheaper and employ a simple design that uses a quarter turn to control fluid flow.
Plug Valve Body
Plug valves are quarter-turn valves that have cylindrical or tapered plugs to control the flow of fluids. The plug valve body is the main component of this type of valve, and it consists of a body, bonnet, and stem. When the valve is closed, the slips on the plug valve expand onto the body seat for protection, allowing for complete shut off. When open, easy flow control is achieved.
Plug valves offer on-off, redirection, and moderate throttling services and can be used as a replacement for gate valves in existing process services. There are several types of plug valves available, including soft seal, oil lubricated hard seal, lift, 3-way and 4-way. Regardless of the type chosen, proper maintenance and care will help ensure optimal performance and longevity when using a plug valve in industrial applications.
Plug Valve Stem
Plug valves are designed to permit or prevent flow in on-off, moderate throttling, and diverting services. The main component of a plug valve is the cylindrical or tapered plug that controls the flow of the fluid. The stem connects the plug to the valve handle, and most plug valves have a top-entry design, allowing for easy maintenance and repair.
The stem also plays an important role in ensuring that the valve operates smoothly and effectively. It helps to guide the movement of the plug and provides stability to prevent damage to the valve body or other components.
Most plug valves have one or more hollow channels positioned horizontally to facilitate easy flow when open. When closed, these channels are sealed off completely by the 100% contact of the plug with the valve body, offering complete shut off. Plug valves with metal bodies can be serviced and repaired without removing the valve from the piping system, making them a practical option for many industrial applications.
Plug Valve Disc
A plug valve is a type of valve that uses a cylindrical or conically tapered plug to control flow. The plug rotates inside the valve body, allowing for precise control over the flow of liquid or gas. One of the advantages of plug valves is that they provide tighter shut-off than ball valves and are more compact, making them ideal for use in smaller departments.
The most important component of a plug valve is the plug valve disc. This disc can be made from a variety of materials depending on the application, such as stainless steel, bronze, or plastic. The shape of the disc can also vary based on its intended use, with some discs being cylindrical and others being conical.
Plug valves have a straight through full port opening which allows for high flow rates and minimal pressure drop. They can be used for on-off, moderate throttling, and diverting services. The slips on the plug expand onto the body seat when closed, protecting the seals from wear and abrasion. Overall, plug valves offer reliable and versatile performance in a range of applications.
Plug Valve Ports
Plug valves consist of several components, including the body, stem, plug, and actuator. The cylindrical or conically tapered plugs rotate inside the valve body to control media flow. One type of plug valve is the multiport plug valve, which has multiple inlet and outlet ports that can be used for diversion or mixing of flows, and can replace several conventional shutoff valves.
There are several types of plug valves available on the market, including lubricated, non-lubricated, multi-port, eccentric, and expanding valves. The multiport design provides simplified piping and installation, more convenient operation than multiple gate valves, and can eliminate the need for costly pipe fittings. Additionally, plug valves come in various port patterns such as round, rectangular, standard diamond, multi-port and Venturi designs. These different port patterns help to ensure that a plug valve is suitable for a wide range of applications across many industries.
Working Principle of a Plug Valve
Plug valves are used to control fluid flow by rotating a cylinder or cone-shaped plug inside the valve body. The plug valve can be used for on-off, redirection, and throttling services. There are different types of plug valves based on their applications, including soft seal, oil-lubricated hard seal, lift, 3-way, and 4-way plug valves.
The plug valve works by using a cylindrical or tapered plug to permit or prevent straight flow with a straight through full port opening. The position of the port in the plug controls the opening through the valve. A 90-degree rotation fully opens or closes the fluid flow.
Plug valves have a simple structure, fast switching, and low fluid resistance. However, they may have poor sealing, large opening and closing force requirements, and are not as efficient as ball valves. Plug valves can replace gate valves in existing process services where fast switching is required.
Rotation of the plug valve
Plug valves are used to control fluid flow and have a quarter-turn rotation to do so. They can be manually actuated by a handle or powered actuator. The cylindrical or conically tapered plug creates 100% contact for complete shut off in the closed position. Plug valves come in cylindrical or conical shapes and can offer on-off, redirection, and throttling services.
The 90° turn of the plug completely stops fluid flow, while a 45° turn drops pressure two times more than normal. The plug’s hollow channels facilitate easy flow when open, while the seals only expand onto the body seat when closed, protecting them from wear and abrasion. Overall, the rotation of the plug valve is essential to its working principle, allowing for precise control over fluid flow.
Flow control in plug valves
Types of Plug Valves
Plug valves are available in a variety of designs and types, each with unique features and benefits. The different types of plug valves include Lubricated, Non-Lubricated, Multi-Port, Eccentric, and Expanding valves. Lubricated and Non-lubricated plug valves are the two main designs available in the market. The Lubricated plug valve design makes use of a lubricant to reduce friction between the sealing surfaces while operating. Multi-Port, Eccentric, and Expanding valves are also types of plug valves but have unique features that set them apart from other designs. The Eccentric Plug Valve is designed to provide bubble-tight shut-off and low torque operation. In contrast, the Expanding Plug Valve operates by expanding or contracting a rubber sleeve inside the valve body that helps in controlling the flow rate.
Lubricated Plug Valves
Plug valves come in various types, each with its own unique features and applications. One type of plug valve is the lubricated plug valve, which uses a lubricant to reduce friction and lower the operating torque of the valve, allowing for better port sealing. Lubricated plug valves are suitable for applications where frequent cycling of the valve is not required.
Other major types of plug valves include multi-port plug valves, eccentric valves, and expanding valves. However, it’s important to note that lubricated plug valves require more maintenance than other types of plug valves due to their reliance on additional lubrication to maintain their sealing capability.
When selecting a lubricant for a lubricated plug valve, it’s important to consider the nature or properties of the media or fluid that will be flowing through the valve. Overall, lubricated plug valves can be a great option for applications where low operating torque and reliable sealing are important factors.
Non-Lubricated Plug Valves
Plug valves come in several different types, each with specific features to suit various applications. One of these types is the non-lubricated plug valve, which provides reduced friction and lower operating torque. Non-lubricated plug valves are suitable for situations where frequent cycling is not needed.
In addition to non-lubricated options, there are three other major types of plug valves: lubricated, eccentric, and multiport. Lubricants used for plug valves should be selected based on the properties of the fluid flowing through the valve. Eccentric plug valves have a unique design that allows them to seal tightly even when debris is present in the fluid being transported. Multiport plug valves have multiple ports that can be used to divert flow in different directions.
Overall, there are many different factors to consider when choosing a plug valve, including its type and lubrication requirements. Understanding these factors can help you select the best valve for your particular application.
Multi-Port Plug Valves
There are various types of plug valves that are used in a range of applications, including water distribution and air conditioning. One type is the multi-port plug valve, which allows for multiple streams of water or gas to flow through it simultaneously. This type of valve is commonly used in industrial settings where large amounts of water or gas need to be controlled.
Multi-port plug valves can be operated manually or automatically and are designed for maximum durability and longevity. They allow for precise control over the flow of materials, making them an essential component in many different industries. Whether used for controlling the flow of coolant in a manufacturing plant or regulating the temperature of a heating system, multi-port plug valves play an important role in keeping processes running smoothly and efficiently.
Eccentric Plug Valves
One major type of plug valve is the eccentric plug valve, which offers greater control of flow thanks to its V-Port plug design. These valves feature cylindrical or conically tapered plugs that are rotated inside the valve body to regulate the flow of media. With 100% contact between the plug and valve body, eccentric plug valves provide complete shut off when in the closed position.
Eccentric plug valves are available in various lubricating and non-lubricating models, allowing for precise flow control in a range of applications. Their unique design makes them well suited for use in situations where accurate control of flow is crucial. Overall, eccentric plug valves are an important type of quarter turn valve that can offer significant benefits in many different settings.
Expanding Plug Valves
One of the major types of plug valves available in the market is the expanding plug valve. These valves have a complex design with multiple components that allow for true double block and bleed function in one valve, preventing wear and abrasion to the seals. Expanding plug valves use a mechanism that rotates between open and closed positions, protecting both seals from the flow path.
These types of plug valves are commonly used in applications that don’t require double isolation to prevent product contamination. The body and seals do not contact each other during rotation, which avoids wear or abrasion to the seals. This makes expanding plug valves a popular choice for industries where safety is paramount, such as in the oil and gas industry.
Plug Valve types by Pattern
Plug valves come in a variety of patterns to suit different applications. The two main designs for Plug Valves are Lubricated and Non-lubricated Plug Valves. Additionally, there are several other types of plug valves including Multi-Port Plug Valve, Eccentric Plug Valve, and Expanding Plug Valve.
Plug valves have one or more channels positioned horizontally to facilitate easy flow while open. They offer on-off, redirection, and basic moderate throttling services. These valves come in either cylindrical or conical shapes, and the body doesn’t contact the seals during rotation. Overall, plug valves provide a reliable and efficient way to control fluid flow in a variety of industrial applications.
Plug Valve Materials
Plug valves are available in a variety of materials, including stainless steel and plastic. The most commonly used materials for making plug valves are stainless steel and plastic. There are four types of plug valves, namely lubricated, non-lubricated, eccentric, and expanding. The two major types of plug valves are lubricated and non-lubricated valves. Plug valves can be made of both metallic and plastic materials, depending on their intended use and application. The material used in the valve’s construction plays a crucial role in determining its durability, resistance to corrosion, temperature tolerance, and pressure ratings.
Pressure Balanced Taper Plug Valves
Plug valves are designed to control the flow of fluids in pipelines. Pressure balanced taper plug valves are designed to prevent taper locking by generating a balancing force that replaces sealant pressure with live line pressure. The valve has a cylindrical or conically tapered plug with one or more hollow passageways that allow media flow control. Plug valves require only a 90° turn for full open or close using mechanical lever activation, unlike gate valves. After a full 90° turn, the plug port becomes perpendicular to the flow, completely stopping fluid flow in plug valves. Throttling is possible in plug valves by rotating the plug to a 45° turn, reducing inlet port flow area and dropping pressure. This simple mechanism makes plug valves ideal for use in various industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment.
Advantages of Plug Valves
Plug valves are employed as isolation valves because of their excellent and tight shut-off abilities. They offer superior sealing performance compared to butterfly and gate valves due to wear on their seat or plug. Multiport plug valves provide additional ports for connections, making them versatile for various applications. For instance, multi-port plug valves with L or T configuration can divert flows or mix flows together, replacing several conventional shutoff valves.
Plug valves come in many types, including lubricated, non-lubricated, multi-port, eccentric, and expanding valves. Lubricated plug valves have a mechanism that helps reduce the friction between the plug and seat, thereby enhancing their durability. Non-lubricated plug valves do not require any lubrication and thus are low maintenance.
In summary, plug valves offer an excellent solution for shutoff applications due to their superior sealing performance and versatility.
Disadvantages of Plug Valves
While plug valves offer better shut-off capability than gate and butterfly valves, they have some disadvantages. Due to the high friction in the valve mechanism, operating plug valves requires more force and often needs an actuator for larger valves. Additionally, they have a higher pressure drop due to their reducing port design.
Furthermore, compared to ball valves of similar design, plug valves are typically more expensive. Despite these drawbacks, plug valves come in different types with unique features such as lubricated, non-lubricated, multi-port, eccentric, and expanding valves. It is important to consider the specific needs of a project before choosing which type of plug valve is best suited for it.
Codes and Standards for Plug Valve Design
Plug valves are commonly used in the industrial sector and come in different sizes and configurations. There are various industry codes and standards governing plug valve design, such as ASME B16.10, API 599, API 6D, and BS 5353. Eccentric plug valves follow MSS SP-108 and AWWA C517 codes and standards.
Four distinct characteristics differentiate plug valves – plug shape, plug opening, lubrication, and number of ports. The valve operates by rotating the plug to control flow through it. There are several instructional videos available online that demonstrate how this works. Plug valves can have alternate designs that comply with industry standards, such as cylindrical plug faces and round ports.
Applications of Plug Valves
Plug valves are commonly used in various industries because of their versatility and durability. They come in a variety of types, including lubricated, non-lubricated, eccentric, and expanding plug valves. Multiport plug valves can function as more than simple shutoff valves because they offer 3-, 4-, and 5-way designs that allow for diverting or mixing flows. Multiport plug valves with “L” or “T” configurations can replace multiple conventional shutoff valves, making them an efficient choice for specific applications.
Additionally, plug valves with different port apertures can be designed for particular uses. For example, lubricated plug valves are suitable for high-pressure applications that require tight sealing capabilities. Non-lubricated plug valves do not require any lubrication and are used in low-pressure applications where a small amount of leakage is acceptable. Eccentric plug valves operate without friction and are ideal for slurries and viscous liquids. Expanding plug valves are designed to provide excellent flow control capabilities while being resistant to wear and tear. Overall, the application of plug valves depends on several factors such as pressure requirements, flow rate, and the type of fluid being controlled.
Comparing Plug Valves to Other Valve Types
Plug valves are versatile and can act as more than just shutoff valves due to their multiple ports. These ports enable multiport plug valves to be designed as 3-, 4-, and 5-way options, making them a perfect replacement for multiple conventional valves. The number of ports, opening mechanism, plug shape, and lubrication are crucial design elements that make plug valves unique. They offer a distinct design and function as compared to ball valves. To learn more about how plug valves work, you can take a video course introducing the topic.
What is the weight of water pressure balance valve
Conclusion
In conclusion, plug valves are versatile and reliable devices that cater to a wide range of applications in various industries. Their simple design, easy maintenance, and high durability make them an ideal choice for many applications. Understanding the working principle, materials used, types available, advantages, and disadvantages of plug valves will help you choose the right one for your needs. Whether it’s for chemical processing, oil and gas production or water treatment plants, choosing the right valve is crucial to ensure optimal performance and long service life. To learn more about how plug valves compare to other valve types and their specific applications in different industries, check out our detailed guide on plug valves.
Mr. Jahangir Alam is an Electrical & Electronics Engineer with a wide range of experience in several fields of Engineering. He finds engineering articles to be very interesting, and that is why he likes to write them. To know more about him, please click here.

